Artemis II Crew Trains on T-38
Artemis II astronauts trained on T-38 jets, which helps prepare them for the rigors of upcoming Moon missions and inspires the public by showing NASA's commitment to safe, successful human spaceflight.
Curious Now
What's new in science
Artemis II astronauts trained on T-38 jets, which helps prepare them for the rigors of upcoming Moon missions and inspires the public by showing NASA's commitment to safe, successful human spaceflight.
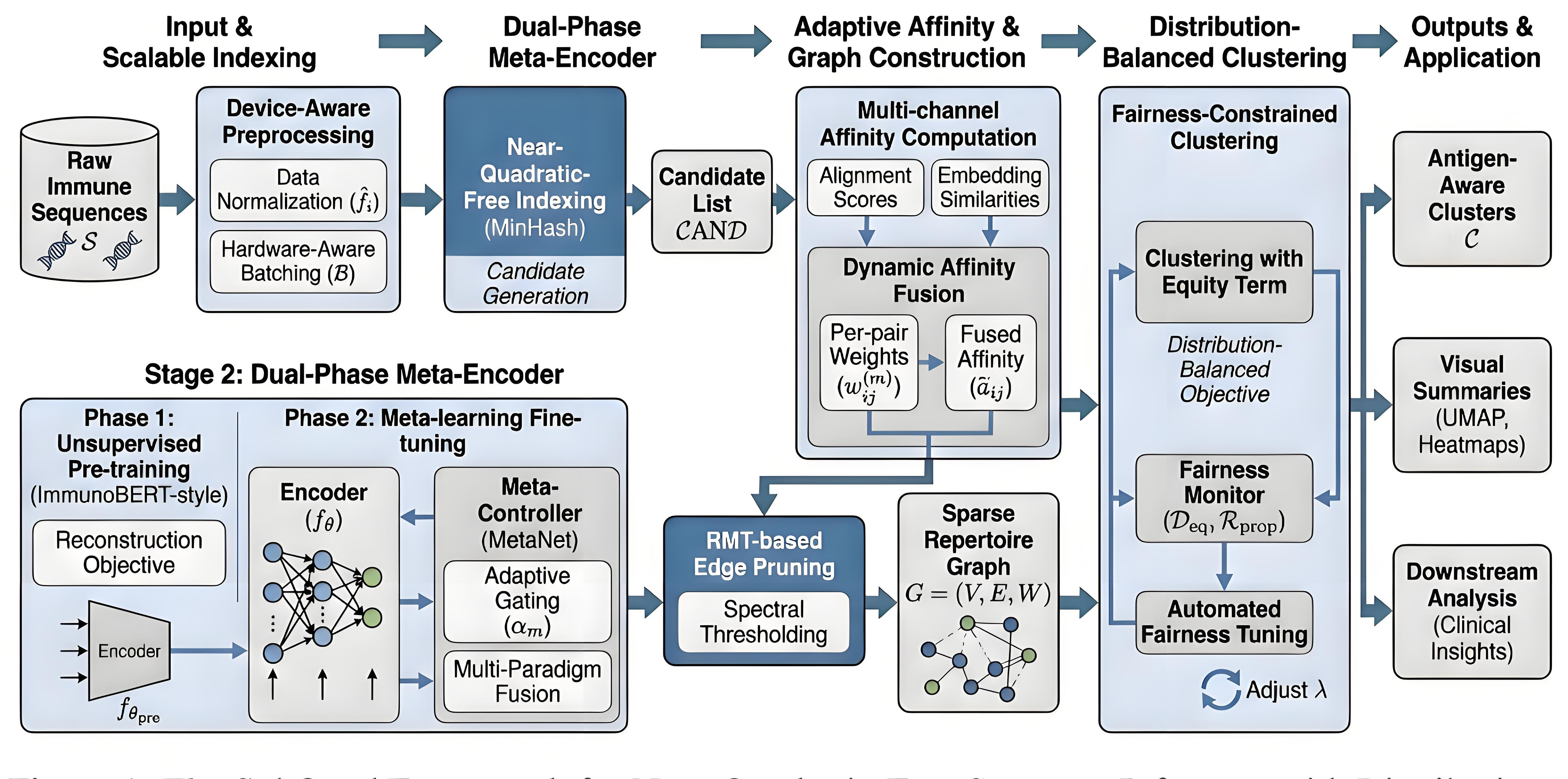
A new algorithm can efficiently analyze immune system data to identify rare but important immune cell types, helping doctors understand immune responses and diseases.
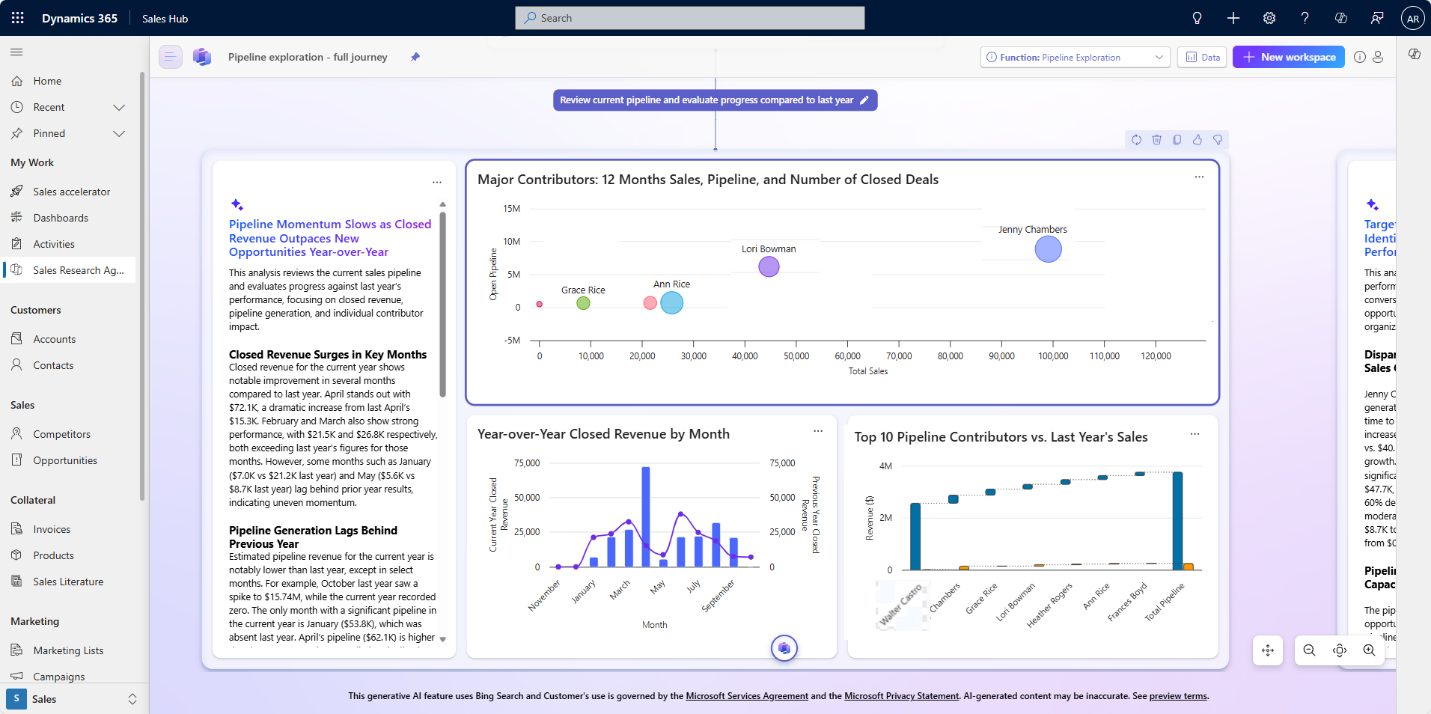
Enterprises can now use an AI agent to quickly find sales data insights, rather than manually searching through CRM systems. This makes sales teams more efficient and helps leaders make better-informed decisions.
Researchers developed a system to improve data collection by UAVs monitoring wildfires, which could help detect and respond to wildfires faster, reducing environmental damage.
Researchers found that AI assistants can subtly distort users' reality, values, and actions in harmful ways. This discovery highlights the importance of developing psychological resilience to potential AI manipulation.
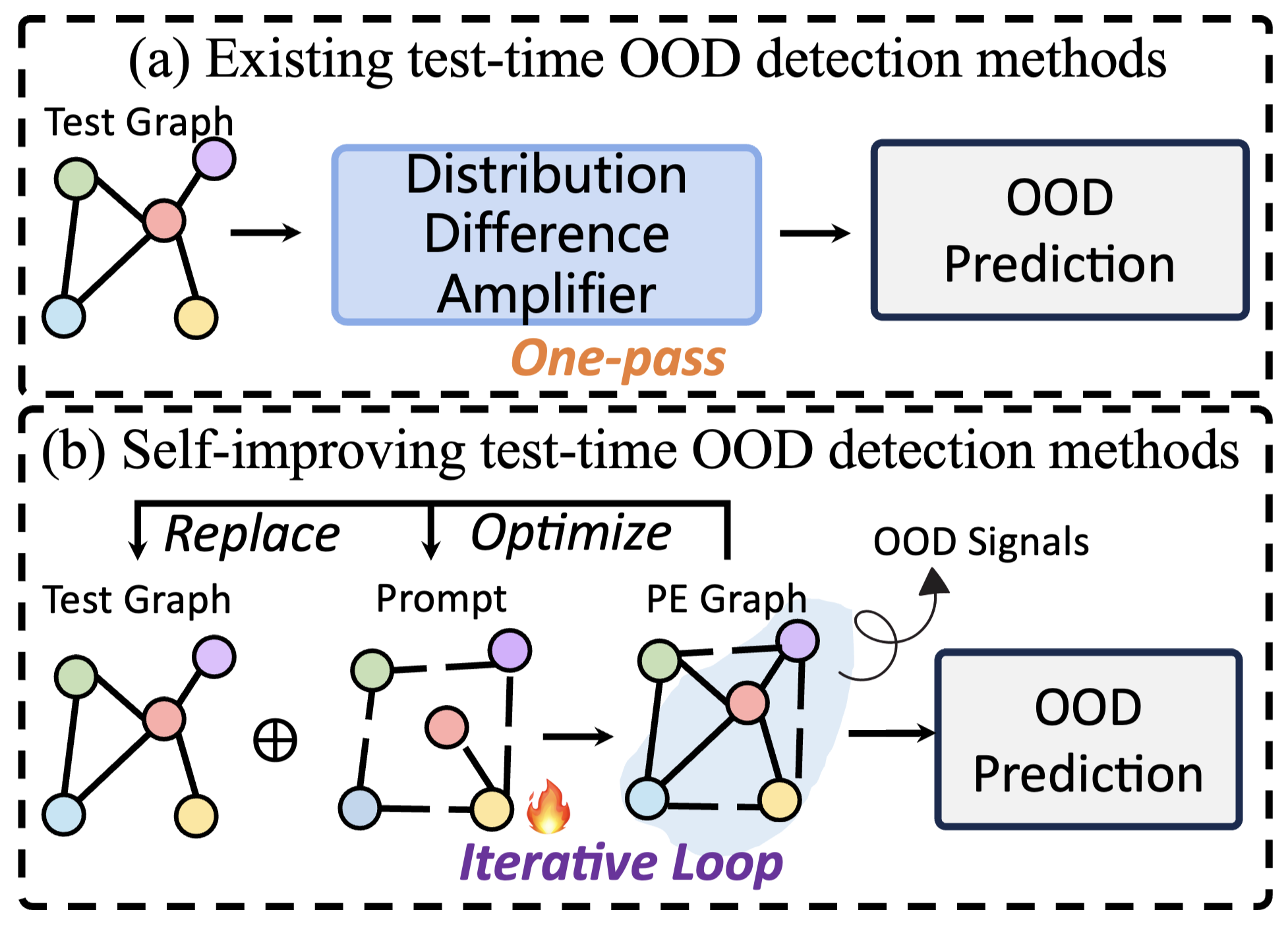
Researchers developed a way to detect when a graph model is being used on data it wasn't trained on, helping ensure the reliability of graph AI systems in real-world applications.
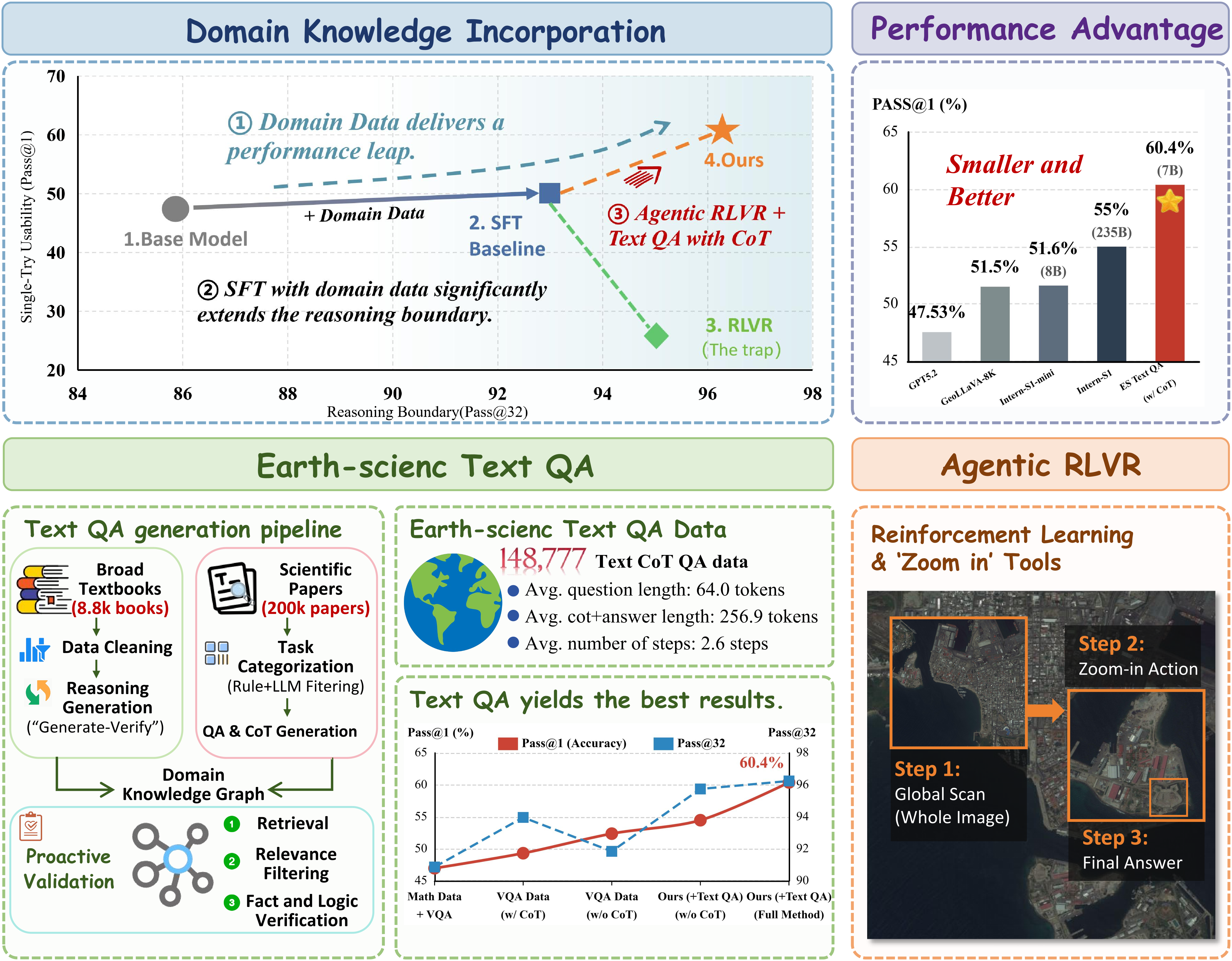
A new AI system can better understand complex satellite images by first learning relevant information through text, before analyzing the visual data. This could improve how we use satellite imagery to study the environment and plan infrastructure.

Researchers found new ways to attack black-box AI language models by exploiting fine-grained details, which could lead to better security measures to protect these powerful systems from abuse.
Researchers developed an advanced algorithm that helps schedule satellite operations even when there is uncertainty about factors like profit, resources, and weather. This could lead to more reliable and flexible Earth observation from satellites.
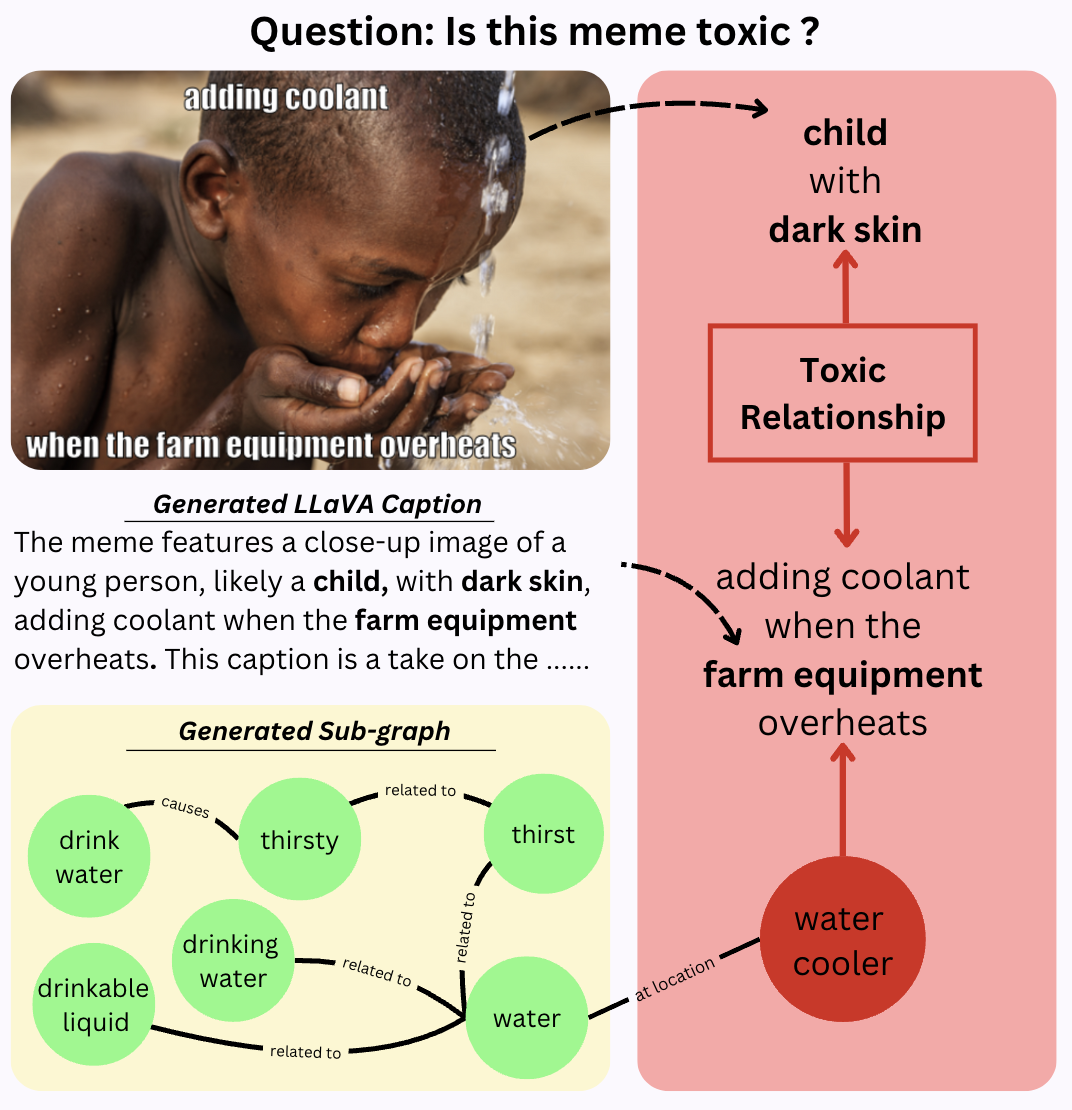
Researchers developed a framework to better detect toxic content online by combining text and images, which could help make social media platforms safer for users.
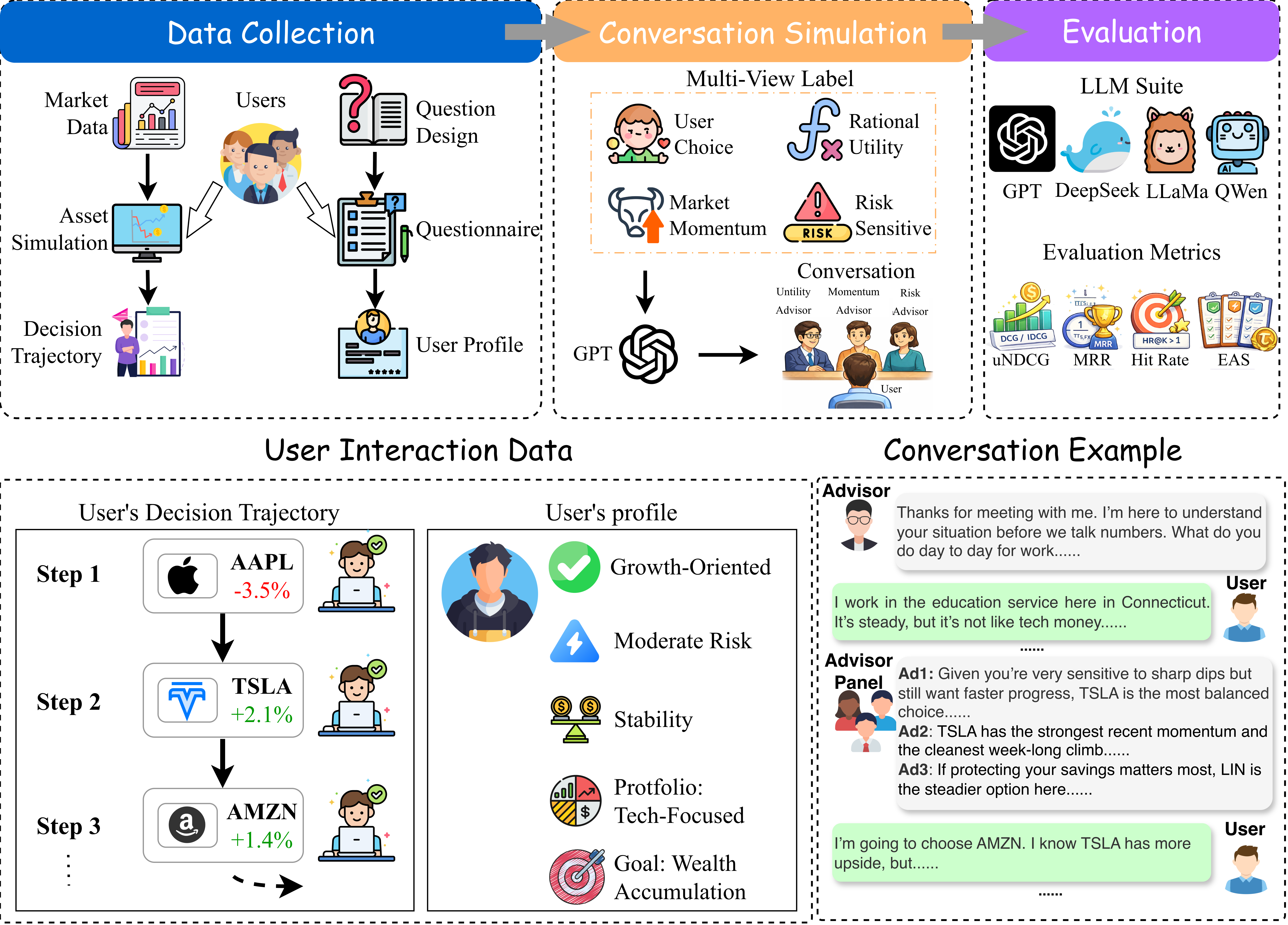
Researchers developed a benchmark to evaluate AI systems that give financial advice, focusing on long-term utility rather than just imitating user behavior, which can be short-sighted in volatile markets.
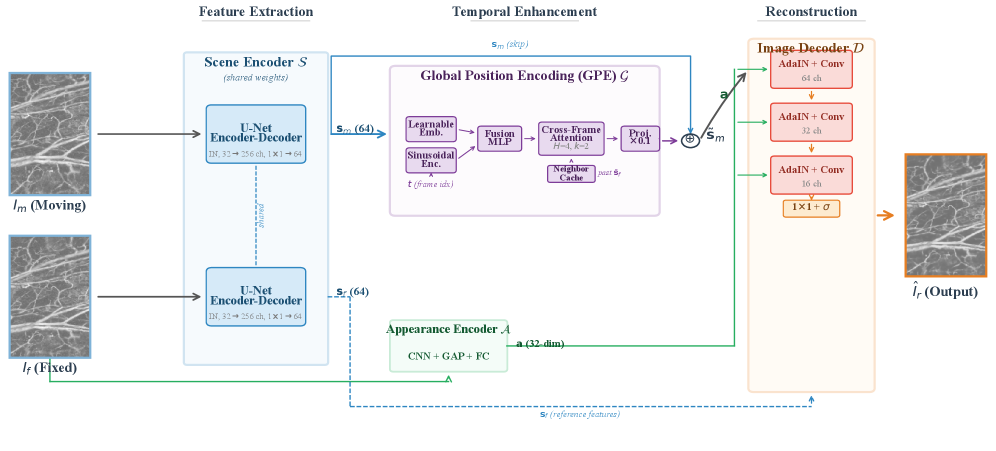
Researchers developed a technique to align microscope images taken from opposite scan directions, which could improve the speed and accuracy of photoacoustic imaging used for medical diagnosis and research.
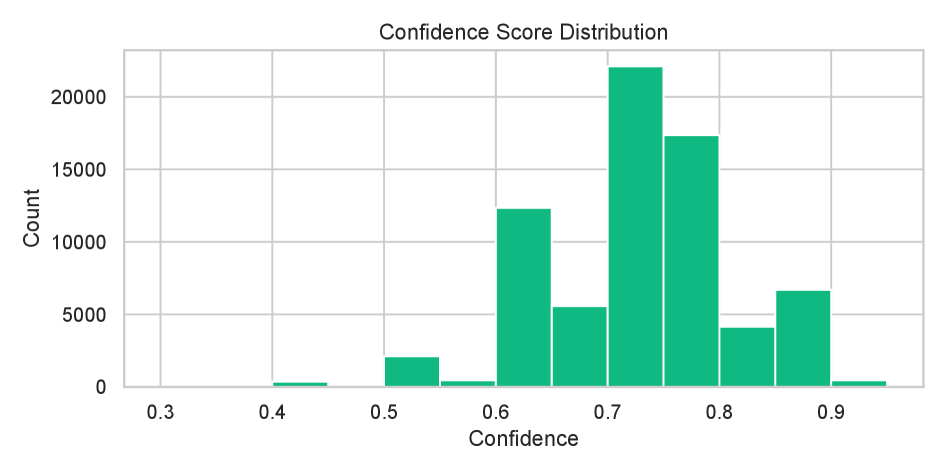
Researchers developed a new algorithm that can analyze patterns of emotion and psychology hidden within classical Persian poetry, offering a new way to understand the emotional lives of people long ago.
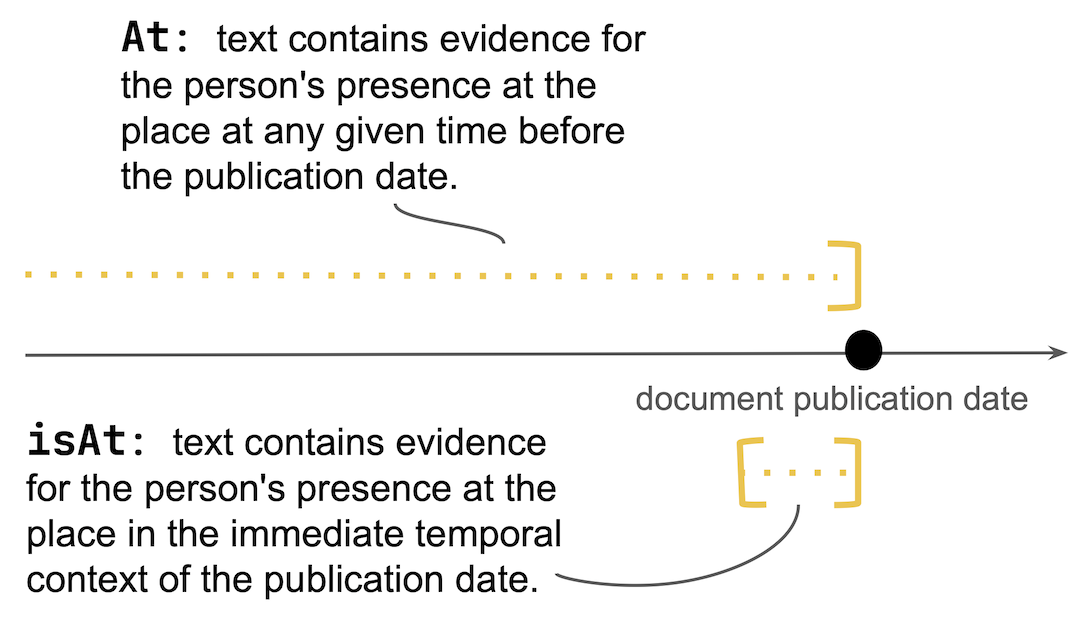
A new CLEF evaluation lab will test how well AI systems can extract information about people and places from old texts written in different languages. This could help historians and journalists better understand the connections between historical figures and locations.
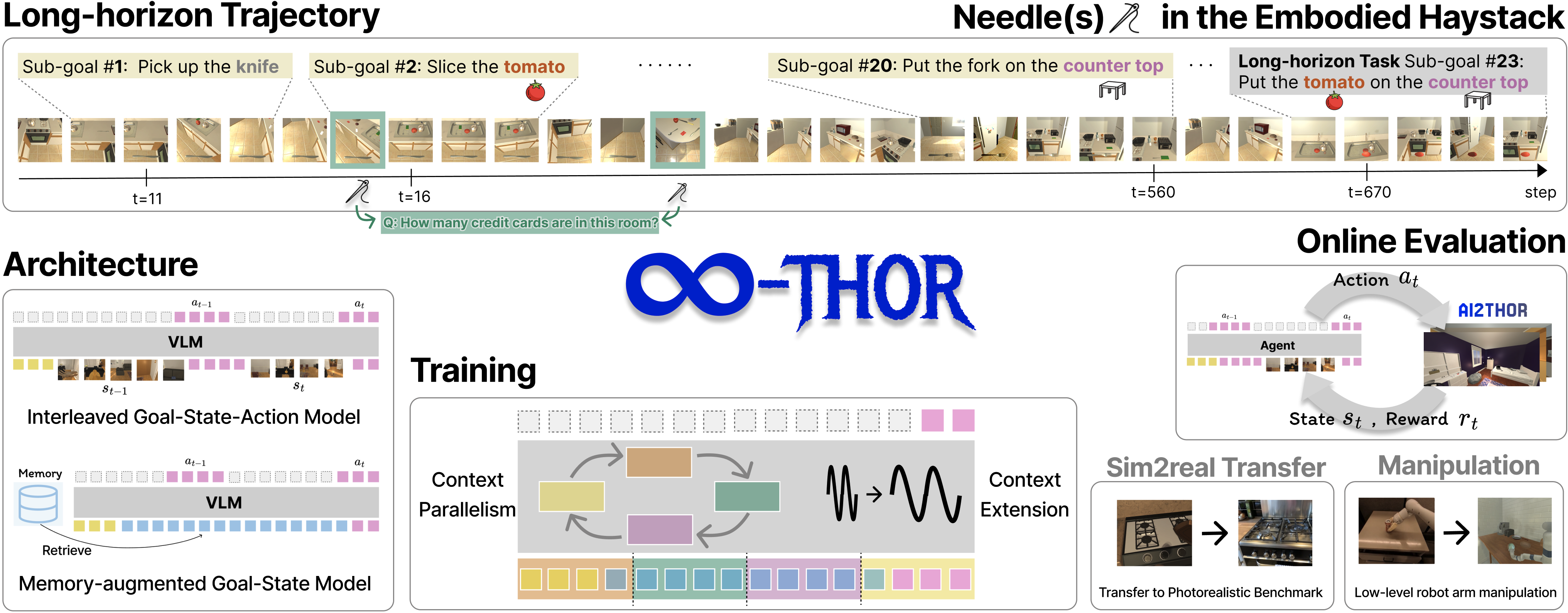
Researchers developed a new framework called $\infty$-THOR that can better understand and reason about long-term contexts in embodied AI systems, which could lead to more capable and contextually-aware AI assistants.
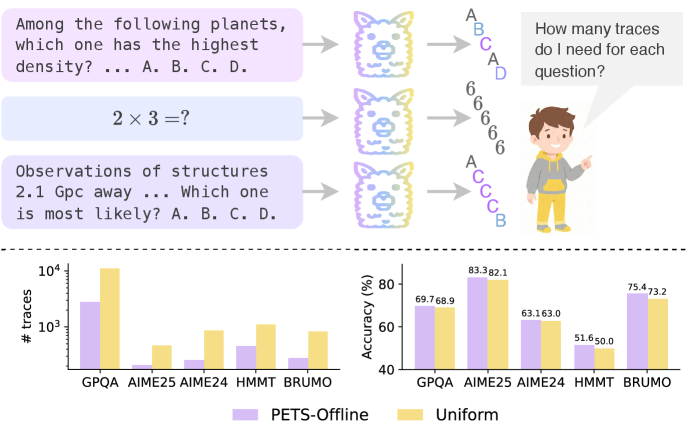
A new framework called PETS helps AI models perform more consistently during testing, which could lead to more reliable and effective AI systems in real-world applications.
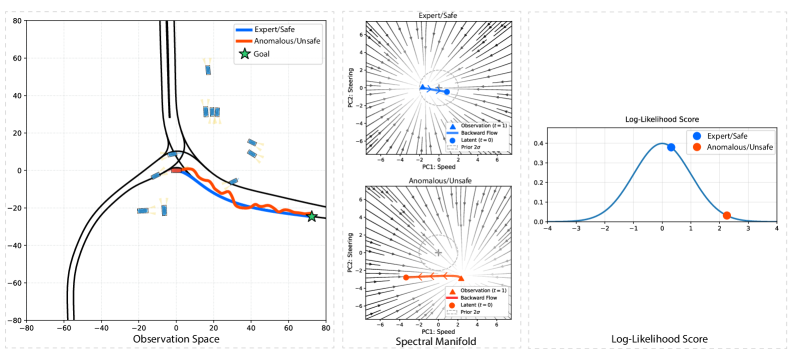
Researchers developed a new method to help self-driving cars continuously detect and avoid rare, risky situations, improving safety for autonomous vehicles.
Researchers developed a new logical framework to model how people interact with information in a structured, dynamic way, which could improve information retrieval and recommendation systems.

Researchers developed a way to spot potential problems before they happen by analyzing patterns in data over time. This could help prevent system failures in fields like industry, finance, and cybersecurity by giving early warnings.
Current speech language models can perform as well as combining speech recognition with language models, without explicit speech recognition. This means these speech models can produce accurate text output from audio inputs more efficiently.